Sunit Singla MD LAB
ARDS Pathobiology and Therapeutics Heading link
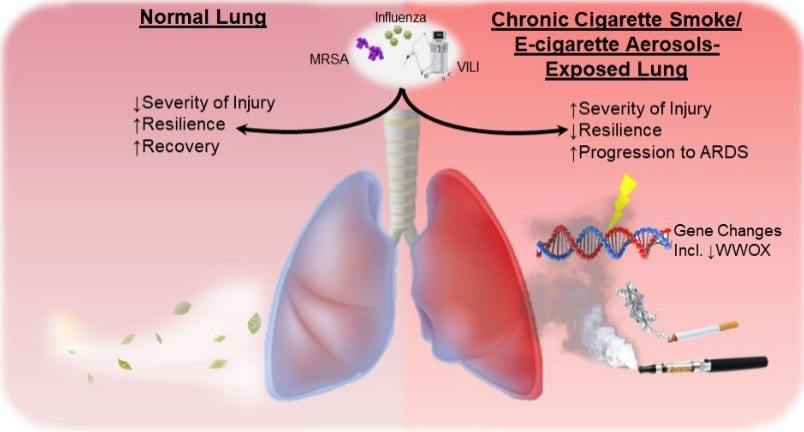
The long-term objective of our lab is to cultivate a program of research that contributes towards maintaining a pipeline of novel therapeutic strategies targeting inflammation and vascular leak during acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Specifically, the approach taken by this research program is to (1) identify dysregulated genes in patients exposed to cigarette smoke and other environmental toxins that may biologically inform the means by which these environmental exposures increase the risk for ARDS, (2) determine the underlying molecular mechanism(s) linking environmental exposures to ARDS risk via identified candidate gene(s), and (3) develop novel candidate gene(s)-based therapeutic strategies that can be tested in available animal models and advanced towards clinical investigations.
Current efforts are focused on several areas along the translational research spectrum:
1) Characterizing novel subsets of patients at increased risk for ARDS
2) Determining the mechanistic contribution of WWOX gene downregulation in smoke/vapor-priming of vascular leak during ARDS
3) Executing a phase IIb clinical trial as part of a multicenter effort to examine the safety and efficacy of therapeutic hypothermia in ARDS
Selected Key Publications Heading link
Zeng Z, Chen W, Moshensky A, Shakir Z, Khan R, Crotty Alexander LE, Ware LB, Aldaz CM, Jacobson JR, Dudek SM, Natarajan V, Machado RF, Singla S. Cigarette Smoke and Nicotine-Containing E-cigarette Vapor Downregulate Lung WWOX Expression Which is Associated with Increased Severity of Murine ARDS. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021 Jan;64(1):89-99. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0145OC. PMID: 33058734; PMCID: PMC7780991.
Singla, Sunit; Chen, Jiwang; Sethuraman, Shruthi; Sysol, Justin R.; Gampa, Amulya; Zhao, Shuangping; Machado, Roberto F. Loss of Lung WWOX Expression Causes Neutrophilic Inflammation. AJP: Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 2017 Mar 10. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 28283473
Singla, Sunit; Sysol, Justin; Dille, Benjamin; Chen, Jiwang; Machado, Roberto F. Hemin Causes Lung Microvascular Endothelial Barrier Dysfunction by Necroptotic Cell Death. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology. 2017 Apr 19. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 28421813
Singla, Sunit; Zhou, Tong; Javaid, Kamran; Zhang, Wei; Ma, Shwu-Fan; Wade, Michael S.; Noth, Imre; Sweiss, Nadera J.; Garcia, Joe G.N.; Machado, Roberto F. Expression Profiling Elucidates A Molecular Gene Signature Which Identifies Pulmonary Hypertension In Sarcoidosis. Pulmonary Circulation. 2016 Dec; 6(4): 465–471. PMCID: PMC5210052
Singla, Sunit; Predescu, Dan; Bardita, Cristina; Wang, Minhua; Zhang, Jian; Balk, Robert A.; Predescu, Sanda. Pro-inflammatory endothelial cell dysfunction is associated with intersectin-1s down-regulation. Respir Res.12; 2011 Apr 12:46.PMID:21486462
Research Heading link
Role of lung WWOX deficiency in vascular leak during lung injury
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a critical illness that afflicts an estimated 200,000 patients/year in the United States alone, kills approximately 75,000, and is seriously debilitating for many survivors. Specific ARDS therapies do not currently exist, and efforts to reduce its burden have been limited by an incomplete characterization of the diverse molecular mechanisms underlying its pathogenesis. The cardinal, morbidity-producing feature of ARDS is non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema resulting from pulmonary vascular barrier disruption with consequent alveolar flooding, and respiratory failure. The conceptual underpinning for these events consists of cytoskeletal contraction of pulmonary endothelial cells (ECs) leading to the formation of paracellular gaps. Novel strategies which reduce the vascular permeability and lung edema of ARDS are desperately needed. The objective of this proposal is to determine the contribution of the tumor suppressor WWOX to the pathobiological processes associated with ARDS. The major goals are to 1) determine the significance of endothelial cell WWOX expression in murine ARDS, 2) define the molecular mechanisms by which WWOX promotes endothelial barrier protection, and 3)establish the conceptual basis for WWOX-based therapy in cigarette-smoke primed, sepsis-induced ARDS.
Zeng Z, Chen W, Moshensky A, Shakir Z, Khan R, Crotty Alexander LE, Ware LB, Aldaz CM, Jacobson JR, Dudek SM, Natarajan V, Machado RF, Singla S. Cigarette Smoke and Nicotine-Containing E-cigarette Vapor Downregulate Lung WWOX Expression Which is Associated with Increased Severity of Murine ARDS. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021 Jan;64(1):89-99. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0145OC. PMID: 33058734; PMCID: PMC7780991.
Singla, Sunit; Chen, Jiwang; Sethuraman, Shruthi; Sysol, Justin R.; Gampa, Amulya; Zhao, Shuangping; Machado, Roberto F. Loss of Lung WWOX Expression Causes Neutrophilic Inflammation. AJP: Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 2017 Mar 10. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 28283473
Risk and Severity of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Following Chronic E-cigarette Aerosols Exposure
The rise of e-cigarette use (vaping) in the United States has been dramatic over the past decade, especially in adolescent and young adult populations. The knowledge gap regarding the adverse health effects of e-cigarette vapor (EV) needs to be addressed urgently to protect public health from an emerging onslaught of potential toxicities associated with chronic exposure. Chronic cigarette smoke (CS) exposure is known to increase the risk and severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). ARDS is a critical illness that afflicts an estimated 200,000 patients/year in the United States alone, with a 46% mortality rate in severe cases. These numbers dramatically increase during respiratory viral pandemics such as the H1N1 influenza pandemic of 2009, and the current coronavirus-related global disaster. A biomarker for increased ARDS susceptibility following CS exposure is a decrease WWOX expression detectable in blood, airway cells, and lung tissue. Mice exposed chronically to e-cigarette aerosols have been found to exhibit decreased lung WWOX expression and an increased severity of ARDS following gram-negative endotoxin instillation in the airways. Activities in this project include 1) utilizing diverse clinically relevant challenges to identify increased ARDS susceptibility induced by e-cigarette aerosols, 2) characterizing variants in EV composition that may enhance priming for ARDS, and 3) identifying viable susceptibility biomarkers for aerosol-induced increases in ARDS risk. The overall goal is to improve scientific knowledge of the toxicity and health effects of e-cigarettes.
Zeng Z, Chen W, Moshensky A, Shakir Z, Khan R, Crotty Alexander LE, Ware LB, Aldaz CM, Jacobson JR, Dudek SM, Natarajan V, Machado RF, Singla S. Cigarette Smoke and Nicotine-Containing E-cigarette Vapor Downregulate Lung WWOX Expression Which is Associated with Increased Severity of Murine ARDS. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021 Jan;64(1):89-99. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0145OC. PMID: 33058734; PMCID: PMC7780991.
Cooling to Help Injured Lungs (CHILL) Phase 2b Randomized Control Trial of Therapeutic Hypothermia in Patients with ARDS
We are part of a multicenter network performing this Phase IIb randomized clinical trial to study the potential benefit and safety of mild hypothermia in patients with ARDS using 28-day ventilator-free days and other clinical and laboratory surrogates for mortality. This study will generate the necessary information to determine whether and how to design a definitive Phase III clinical trial of therapeutic hypothermia to reduce mortality in patients with ARDS. This trial will compare mild hypothermia (34°-35°C) plus neuromuscular blockade vs. standard temperature management in patients with moderate to severe ARDS.
Clinical Trials
Lab Members Heading link
Weiguo Chen, MD/PhD
Research Assistant Professor
weiguo@uic.edu
Malvika Kaul, MD
Mkaul2@uic.edu
Hannah Carlson
Clinical Research Coordinator – CHILL Study
hrc@uic.edu
Former Trainees Heading link
Visiting Professor:
Zhenguo Zeng, MD/PhD August, 2018 – August, 2019
First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Jiangxi, China
Associate Professor of Medicine
Zeng, Zhenguo; Chen, Weiguo; Moshensky, Alexander; Shakir, Zaid; Khan, Raheel; Crotty-Alexander, Laura; Ware, Lorraine B.; Aldaz, Marcelo; Jacobson, Jeffrey R.; Dudek, Steven M.; Natarajan, Vishwanathan; Machado, Roberto F.; Singla, Sunit. Cigarette Smoke and Nicotine-Containing E-cigarette Vapor Downregulate Lung WWOX Expression Which is Associated with Increased Severity of Murine ARDS. Am J Respir Cell Mol Bio. 2021 Jan;64(1):89-99. PMID: 33058734
Singla, Sunit; Zeng, Zhenguo; Chen, Weiguo; Demeritte, Regaina; Chen, Jiwang; Jacobson, Jeffrey R.; Dudek, Steven M.; Natarajan, Vishwanathan; Machado, Roberto F. Endothelial-Specific Knockdown of Lung WWOX Expression Worsens Acute Lung Injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2019; 199:A4398.
Fellows:
Benjamin Dille, MD 2016-17
Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago
Singla, Sunit; Sysol, Justin; Dille, Benjamin; Chen, Jiwang; Machado, Roberto F. Hemin Causes Lung Microvascular Endothelial Barrier Dysfunction by Necroptotic Cell Death. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology. 2017 Apr 19. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 28421813
Zaid Shakir, MD 2016-18
Pulmonary/Critical Care Medicine, University of Illinois at Chicago
Zeng, Zhenguo; Chen, Weiguo; Moshensky, Alexander; Shakir, Zaid; Khan, Raheel; Crotty-Alexander, Laura; Ware, Lorraine B.; Aldaz, Marcelo; Jacobson, Jeffrey R.; Dudek, Steven M.; Natarajan, Vishwanathan; Machado, Roberto F.; Singla, Sunit. Cigarette Smoke and Nicotine-Containing E-cigarette Vapor Downregulate Lung WWOX Expression Which is Associated with Increased Severity of Murine ARDS. Am J Respir Cell Mol Bio. 2021 Jan;64(1):89-99. PMID: 33058734
Singla, Sunit; Shakir, Zaid; Gomes, Marta T.; Jones, Nicole M.; Natarajan, Vishwanathan; Machado, Roberto F. Cigarette Smoke Exposure Induces Loss of Lung WWOX Expression Which Is Associated with Increased Vascular Leak During ARDS. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2018;197: A2471.
Students (MD, PhD, Undergraduate):
Amulya Gampa, MD Medical Student Summer, 2013
University of Illinois at Chicago
Chief resident at University of Chicago
Singla, Sunit; Chen, Jiwang; Sethuraman, Shruthi; Sysol, Justin R.; Gampa, Amulya; Zhao, Shuangping; Machado, Roberto F. Loss of Lung WWOX Expression Causes Neutrophilic Inflammation. AJP: Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 2017 Mar 10. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 28283473
Shruthi Sethuraman Undergraduate Summer, 2016
Ohio State University
Went on to work in the labs of John Christman, MD and Megan Ballinger, PhD
Presented at ATS in 2018
Now medical student at Ohio State University
Singla, Sunit; Chen, Jiwang; Sethuraman, Shruthi; Sysol, Justin R.; Gampa, Amulya; Zhao, Shuangping; Machado, Roberto F. Loss of Lung WWOX Expression Causes Neutrophilic Inflammation. AJP: Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 2017 Mar 10. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 28283473
Collaborators
Laura E. Crotty Alexander, MD
Associate Professor of Medicine
University of California, San Diego
C. Marcelo Aldaz, MD/PhD
Professor of Medicine
MD Anderson
University of Texas
Roberto F. Machado, MD
Professor of Medicine
Indiana University
Jeffrey D. Hasday, MD
Professor of Medicine
University of Maryland
Lorraine B. Ware, MD
Professor of Medicine
Vanderbilt University
