Jeffrey R. Jacobson, MD LAB
Mechanisms of Lung Vascular Inflammatory Responses Heading link
Lab News: Awarded Grants:
- A Phase 2a, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to assess the efficacy and safety of ALT-100 in patients with moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
- 5R01HL147942 Sphingolipids as Novel Therapeutic Targets in Radiation Lung Injury
- P0HL126609 Cytoskeletal Regulation of Lung Endothelial Pathobiology in ARDS
- 5R38HL155729 Fostering Academic Physician-Investigators Treating High Risk Populations
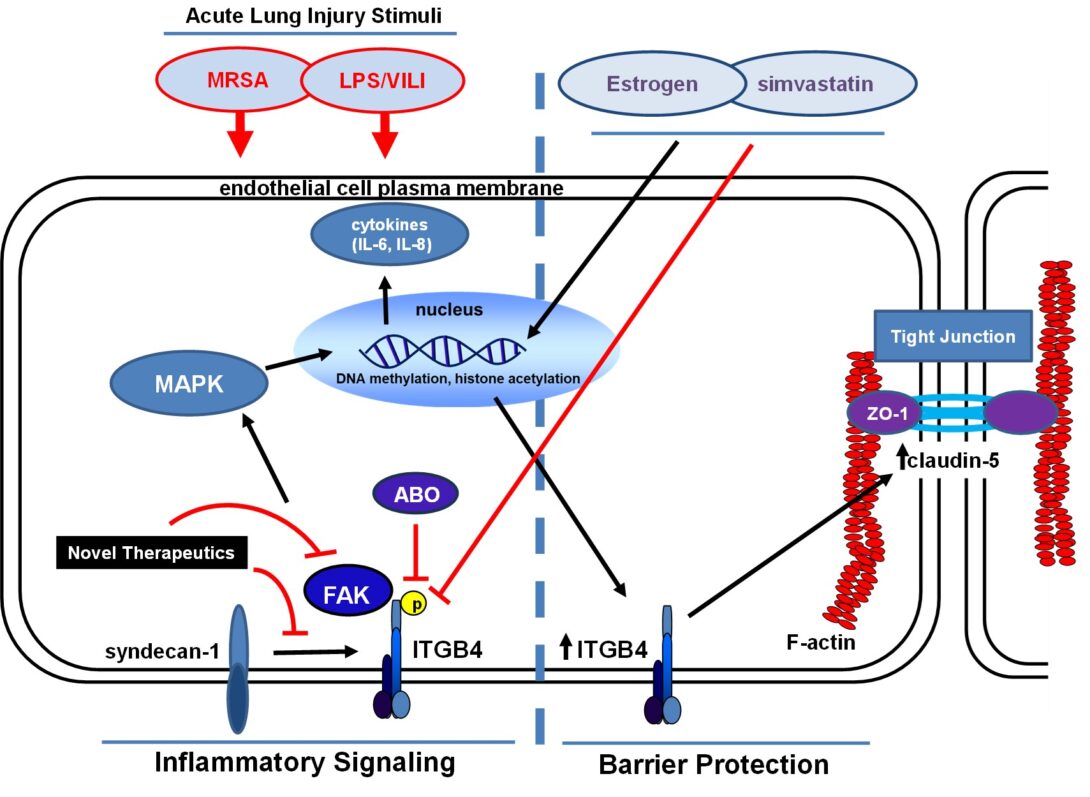
Dr. Jacobson is a pulmonary and critical care physician-scientist with research interests in cell and animal models of acute lung injury (ALI), ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) and radiation-induced lung injury, with ongoing research in this area currently supported by the NHLBI (R01 HL147942, PI: Jacobson). He is also Senior Associate Head of the Department of Medicine and Director of the Medical Intensive Care Unit (MICU) at the University of Illinois Hospital (UIH). Most recently, the Jacobson lab research has focused on the role of integrin β4 (ITGB4) in vascular inflammatory responses and was the first to characterize ITGB4 as an inflammatory mediator that is dramatically upregulated by statin drugs in both cell and pre-clinical models of inflammatory lung injury. Additionally, lab research has identified a novel ITGB4-mediated signaling pathway that regulates lung endothelial cell (EC) barrier enhancement induced by sphingosine 1-phosphate and hepatocyte growth factor, agonists that also confer protection in pre-clinical models of ALI. The Jacobson lab has also identified inhibitors of focal adhesion kinase (FAK), a molecule regulated by ITGB4 that has been implicated as a mediator of both increased and decreased barrier integrity, as protective in ALI models. Much of the ongoing research is aimed at understanding mechanisms responsible for ITGB4 regulation of EC signaling and inflammatory responses in ALI and involves active collaborations with colleagues at UIC and beyond.
Key Publications Heading link
Key Publications
1. Endothelial signaling and barrier regulation by statins. Our lab was among the first to report the barrier-protective effects of statin drugs in both in vitro and in vivo models of acute lung injury. We subsequently identified a number of mechanisms critical to these effects including alterations in EC gene expression, differential Rho GTPase signaling as well as EC signaling mediated by integrin β4 and claudin-5. I personally designed, conducted, and interpreted the majority of the experiments involved in this studies and was primarily responsible for the preparation of the resulting manuscripts. This work has led to novel insights into mechanisms of endothelial cell signaling and barrier regulation in general and has since led directly to a number of other areas of investigation detailed below.
- Jacobson JR, Barnard JW, Grigoryev DN, Ma SF, Tuder RM, Garcia JGN. Attenuation of vascular leak and differential gene expression by simvastatin in a murine model of acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2005, 288(6):L1026-1032.
- Chen W, Pendyala S, Natarajan V, Garcia JGN, Jacobson JR. Simvastatin-mediated endothelial cell barrier protection: GTPase regulation and NADPH oxidase inhibition. Am J Phsyiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2008, 295(4): L575-83. PMCID: PMC2575942
- Chen W, Sammani S, Mitra S, Ma SF, Garica JG, Jacobson JR. Critical role for integrin β4 in the attenuation of murine acute lung injury by simvastatin. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2012, 303(4): L279-285. PMCID: PMC3423831
- Chen W, Sharma R, Rizzo AN, Siegler JH, Garcia JGN, Jacobson JR. Role of claudin-5 in the attenuation of murine acute lung injury by simvastatin. Am J Resp Cell Mol Biol 2014, 50(2): 328-36. PMCID: PMC393094\
2. Molecular mechanisms of acute lung injury (ALI). We have conducted a number of studies exploring other novel mediators of EC permeability in both in vitro and in vivo models of ALI. This work has included a variety of molecular pathways two examples of which are signaling regulated by sphingosine 1-phosphate, a circulating bioactive phospholipid, and adenosine triphosphate. While this work largely represents collaborations with other investigators in our lab, there were individual experiments in each such project for which I was solely responsible for their design and conduct. I was also directly involved in the preparation of each of the resulting manuscripts. These studies collectively provide the basis for ongoing research by our lab and others focused on potential novel therapeutic targets and strategies for patients with acute lung injury.
- Jacobson JR, Dudek SM, Singelton P, Kolosova IA, Verin AD, Garcia JGN. Endothelial cell barrier enhancement by ATP is mediated by the small GTPase Rac and cortactin. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2006, 291(2): L289-95. PMID: 16825658
- Chen W, Garcia JGN, Jacobson JR. Integrin β4 attenuates SHP-2 and MAPK signaling and reduces human lung endothelial inflammatory responses. J Cell Biochem 2010, 110(3): 718-24. PMID: 20512931
- Mitra S, Epshtein Y, Sammani S, Quijada H, Chen W, Bandela M, Desai AA, Garcia JGN, Jacobson JR. UCHL1, a deubiquitinating enzyme, regulates lung endothelial cell permeability in vitro and in vivo. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2021, 320(4):L497-507. PMCID: PMC8238159
- Colamonici M, Epshtein Y, Chen W, Jacobson JR. Haldol attenuates lung endothelial cell permeability in vitro and in vivo. Cells 2021, 10(9): 2186. PMCID: PMC846828
3. Genetics of acute lung injury (ALI). Beyond our interest in the molecular mechanisms of ALI we have also studied the genetic basis of ALI and have identified specific genes of interest in this regard. Collectively, this work represents a highly novel and previously unexplored area of investigation that has led to an increased understanding of the mechanisms underlying differential responses to lung injury stimuli specific to various patient populations.
- Jacobson JR, Dudek SM, Birukov KG, Ye SQ, Girgis R, Garcia JGN. Cytoskeletal activation and altered gene expression in endothelial cells by simvastatin. Am J Resp Cell Molec Biol 2004, 30(5):662-670.
- Zhang LQ, Ma SF, Grigoryev D, Lavoie TL, Xiao HQ. Setterquist R, Li H, Jacobson J, Garcia JG, Ye SQ. Temporal gene expression analysis of human coronary artery endothelial cells treated with simvastatin. Gene Expr 2008, 14(4):229-39.
- Mekontso Dessap A, Voiriot G, Zhou T, Marcos E, Dudek SM, Jacobson JR, Machado R, Adnot S, Brochard L, Maitre B, Garcia JG. Conflicting physiological and genomic cardiopulmonary effects of recruitment maneuvers in murine acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2012, 46(4):541-50. PMCID: PMC3359949
- Sun X, Ma SF, Wade MS, Acosta-Herrera M, Villar J, Pino-Yanes M, Zhou T, Liu B, Belvitch P, Moitra J, Han YJ, Machado R, Noth I, Natarajan V, Dudek SM, Jacobson JR, Flores C, Garcia JG. Functional promoter variants in sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 3 associate with susceptibility to sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2013, 305(7): L467-77. PMCID: PMC4073968
4.GADD45a as a novel candidate acute lung injury (ALI) gene. Our interest in genomic mechanisms of ALI led to a specific focus on GADD45a (growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible alpha). We reported that GADD45a expression levels are associated with murine susceptibility to ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) and is linked to effects on Akt ubiquitination mediated by UCHL1, a deubiquitinating enzyme. In addition, we identified genetic variants in humans associated with risk for ALI. I have been directly involved in all facets of this research and continue to serve as lead investigator on ongoing studies derived from this project.
- Meyer NJ, Huang Y, Sammani S, Singleton PA, Moreno-Vinasco L, Moitra J, Evenoski CL, Hussain AN, Jacobson JR, Lussier YA, Garcia JGN. Gadd45α is a novel acute lung injury candidate gene which influences ventilator-induced lung injury: role of Akt signaling. FASEB J 2009, 23(5):1325-37. PMCID: PMC2669422
- Mitra S, Sammani S, Wang T, Boone DL, Meyer NJ, Dudek SM, Moreno-Vinasco L, Garcia JG, Jacobson JR. Role of GADD45a in Akt phosphorylation and ubiquitination following mechanical stress-induced vascular injury. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 2011, 184(9):1030-1040. PMCID: PMC3763933
- Mitra S, Wade MS, Sun X, Moldobaeva N, Flores C, Ma SF, Zhang W, Garcia JGN, Jacobson JR. GADD45a promoter regulation by a functional genetic variant associated with acute lung injury. PLoS One 2014, 18;9(6):e100169. PMCID: PMC4062486
- Mathew B, Takekoshi D, Sammani S, Epshtein Y, Sharma R, Smith BD, Weichselbaum RR, Garcia JGN, Jacobson JR. Role of GADD45a in murine models of radiation and bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2015, 309(12):L1420-9. PMCID: PMC468331
5. Novel mechanisms of radiation-induced lung injury (RILI). I was primarily responsible for the design and characterization of a murine model of RILI that is now routinely employed by our lab for the study of mechanisms responsible for RILI. We have identified signaling by sphingolipids as a critical mediator of lung responses to radiation implicating these pathways as potential therapeutic targets. While the study of therapeutic strategies to treat patients with RILI represents an unmet medical need, this research has led to the identification of statin drugs, via effects on sphingolipids, as having potentially protective effects in this context. Further, we have identified a critical role for UCHL1 (ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal esterase L1), a deubiquitinating enzyme, in the regulation of sphingolipids affected by radiation in vivo and in vitro and as a key mediator of lung vascular permeability.
- Mathew B*, Jacobson JR*, Berdyshev, Huang Y, Sun X, Zhao Y, Gerhold LM, Siegler J, Evenoski C, Wang T, Zhou T, Zaidi R, Moreno-Vinasco L, Bittman R, Chen CT, Lariviere PJ, Sammani S, Lussier YA, Dudek SM, Natarajan V, Weichselbaum RR, Garcia JG. Role of sphigolipids in murine radiation-induced lung injury: protection by sphingosine 1-phosphate analogs. FASEB J 2011, 25(10):3388-400. *co-first authors. PMCID: PMC3177585
- Mathew B, Jacobson JR, Siegler JH, Moitra J, Blasco M, Xie L, Unzueta C, Zhou T, Evenoski C, Al-Sakka M, Sharma R, Huey B, Bulent A, Smith A, Jayaraman S, Reddy NM, Reddy SP, Fingerle-Rowson G, Bucala R, Dudek SM, Natarajan V, Weichselbaum RR, Garcia JG. Role of migratory inhibition factor in age-related susceptibility to radiation lung injury via NF-E2-related factor-2 and antioxidant regulation. Am J Resp Cell Mol Biol 2013, 49(2): 269-78. PMCID: PMC3824032
- Mathew B, Takekoshi D, Sammani S, Epshtein Y, Sharma R, Smith BD, Weichselbaum RR, Garcia JGN, Jacobson JR. Role of GADD45a in murine models of radiation and bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2015, 309(12):L1420-9. PMCID: PMC46833
- Epshtein Y, Mathew B, Chen W, Jacobson JR. UCHL1 regulates radiation lung injury via sphigosine kinase-1. Cells 2023, 12(19): 2405. PMCID: PMC10572187
Active Research
Sphingolipids as Novel Therapeutic Targets in Radiation Lung Injury
Radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) is a common complication in patients administered thoracic radiotherapy that is associated with significant morbidity and mortality and for which effective therapies currently do not exist. We have developed a mouse model of RILI and identified signaling by sphingolipids as an important mediator of injury. In this proposal, studies will investigate mechanisms of sphingolipid-mediated lung injury in response to radiation which may ultimately yield more precise and effective RILI therapeutic strategies.
Total Award: $1,599,000
Project Period: 04/2020 – 03/2024
Project Role: Principal Investigator
Fostering Academic Physician-Investigators Treating High Risk Populations
The main goal of the UIC StARR Program, an NHLBI-funded career development program, is to recruit internal medicine residents of varied backgrounds and experiences to undergo mentored clinical/translational research training related to the areas of cardiovascular, pulmonary, or hematologic diseases that will foster opportunities to help lead the next generation of highly diverse and skilled physician-investigators in the biomedical sciences.
Total Award: $1,339,937
Project Period: 8/2021 – 6/2025
Project Role: Multi-Principal Investigator
Pathobiology of MRSA-induced Endothelial Permeability and Acute Lung Injury
This project addresses the contribution of unchecked endothelial cell (EC) permeability to the devastating multi-organ failure and mortality of ARDS by providing a comprehensive understanding at the molecular and genomic level of vascular barrier regulation and repair. Proposed are four highly clinically-relevant, tightly-woven Projects centered on specific lung EC target proteins/genes that are involved in: i) the unchecked vascular permeability and injury in ARDS; ii) vascular responses to excessive mechanical stress in VILI; iii) contributing to the genetic basis for ARDS health disparities in African descent subjects; and, iv) providing novel ARDS therapeutic opportunities.
Total Award: $1,798,869 $516,064 for Co-I portion
Project Period: 9/2023 – 8/2027
Project Role: Sub Site Co- Investigator
Current Lab Members
Weiguo Chen, M.D., Ph.D.
Yulia Epshtein, Ph.D.
Former Trainees
Michael Blasco, B.S., pre-medical student (2010-2011).
Project title: Role of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor-2 in Radiation-Induced Lung Injury.
Rajesh K. Sharma, M.D., post-residency research (2011-2012).
Project title: Role of PF-573,228, an Inhibitor of Focal Adhesion Kinase, in Endothelial Cell Barrier Protection *abstract presented at 2013 American Thoracic Society International Meeting
Daisuke Takekoshi, M.D., UIC pulmonary/critical care fellow (2011-2013).
Project title: Role of Macrophage Inhibitory Factor in Lung Injury and Fibrosis *co-first author on paper published in Am J Phyiol Lung Cell Mol Biol).
Xiuqin Ni, M.D., Ph.D., visiting postgraduate student (2012-2013). Project title: Interaction of integrin β4 with S1P Receptors in Endothelial Barrier Regulation *first author on paper published in J Cell Biol
Patrick Naureckas, B.S., pre-medical student (2012-2014 summers).
Project title: Endothelial Barrier Responses to Inhibition of c-Abl by Imatinib *co-author on paper published in Am J Phyiol Lung Cell Mol Biol
Paul Lederer, M.D., UIC pulmonary/critical care fellow (2013-2017).
Project title: Role of Focal Adhesion Kinase in Endothelial Barrier Regulation.*first author paper published in Vascul Pharmacol
Mariam Anis, M.D., UIC pulmonary/critical care fellow (2017-2020)
Project title: Sphingosine Kinase as a Modulator Pulmonary Hypertension*first author paper published in Int J Mol Sci
Priyanki Gajwani, B.S., Ph.D. candidate in Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology at UIC, thesis committee member (2021-2022). Thesis title: “Metabolic Responses of the Vascular Endothelium to Inflammatory Injury”
Marco Colamonici, M.D., UIC internal medicine chief resident (2019-2022)
Project Title: Claudin-5 as a Novel Therapeutic Target in Acute Lung Injury *first author on paper published in Cells
Kai Huang, B.S., Ph.D candidate in Biomedical Engineering at UIC, thesis committee member (2022-2023). Thesis title: “Immune Dysregulation in Inflammatory and Autoimmune Disorders”
