The Research in Endocrinology and Cardiometabolic Health Lab
REACH Lab Overview Heading link

Assistant Professor
Email: amahmo4@uic.edu
Office Number: 312.355.8099
In REACH Lab we strive to better understand the role of adipose tissue secretions in the initiation and progression of human diseases with the ultimate goal of identifying novel therapeutic targets and preventive strategies for obesity-related diseases. We seek to accomplish this goal via conducting interdisciplinary research with translational potential in obesity and related morbidities including diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and hormone-dependent malignancies. A major research focus in our lab is endothelial cell dysfunction as an underlying mechanism in the pathogenesis of a wide range of obesity-associated diseases, including peripheral vascular disease, stroke, heart disease, diabetes, insulin resistance, and tumor invasion and metastasis. Our present research focuses on unraveling multiple molecular and epigenetic processes to better understand the multidimensional crosstalk between adipocytes and endothelial cells.
Contact information:
REACH Lab
Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism
835 S Wolcott Ave, 6th Floor, E602
Medical Sciences Building (North Entrance)
Chicago, IL 60612
Lab Phone Number: (312) 355-8565
Meet the PI Heading link
Dr. Abeer Mohamed is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism (College of Medicine, UIC). She received her MD degree and residency training as a Pathologist from Assiut University, Egypt. She served as a surgical/clinical pathologist at South Egypt Cancer Institute (2002-2008), before realizing her true passion was in biomedical research. She earned her Ph.D. in Pathology (College of Medicine, UIC, 2013) where she studied chemoprevention in prostate cancer. For her postdoctoral research (College of Applied Health Sciences, UIC, 2013-2017), she studied physiological and molecular outcomes of lifestyle interventions at the metabolic and vascular levels. She is currently funded by NIH/NHLBI-K99 “DNA Methylation and Vascular Function in Obesity: Role of Exercise and Weight Loss” to study blood and tissue DNA methylation profiles among those who are morbidly obese and the impact of these profiles on metabolic and vascular functions. She is also funded by the NIDDK/NIH-sponsored Diabetes Research and Training Center to study the role of adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicles in diabetes-associate endothelial dysfunction and by University of Illinois’ Cancer Center to study the role of adipose tissue-derived extracellular vesicles in promoting breast cancer metastasis. Dr. Mohamed’s long-term goal is to identify clinically relevant epigenetic mechanisms to help mitigate the increased risk of obesity co-morbidities.
Research Projects Heading link
-
Project 1
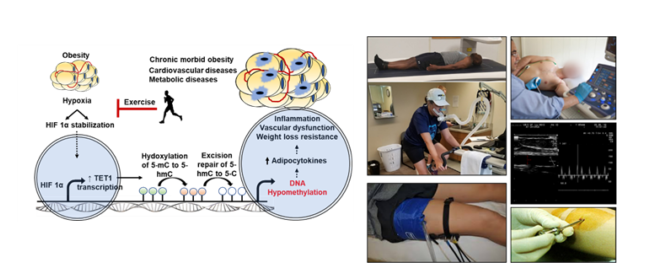
Adipokine DNA hypomethylation and vascular dysfunction in obesity. The link between obesity and cardiovascular disease (CVD) is directly related to the accumulation of dysfunctional adipose tissue that secretes several inflammatory cytokines (adipokines). Epigenetic mechanisms such as DNA methylation enable the body to respond quickly to environmental changes and may represent a mechanistic link between obesity and CVD and serve as valid therapeutic targets. We are investigating gene-specific, and genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in the adipose tissues of obese/diabetic patients compared with healthy individuals and how these patterns correlate with clinical findings and cardiometabolic risk factors. Upstream key players in this pathway are the hypoxia-inducible factor, HIF1α and the DNA hydroxymethylase, ten-eleven translocation-1 (TET1). Exercise and weight loss are also being studied for their effects on restoring normal methylation patterns.
-
Project 2
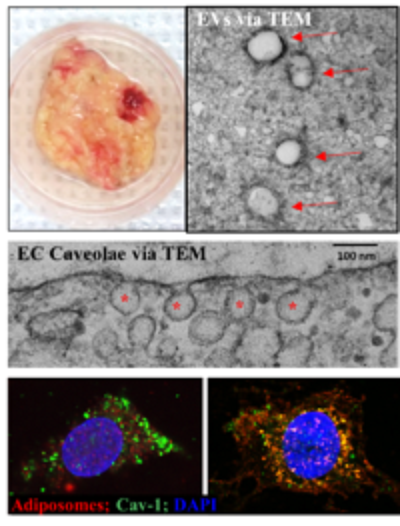
Role of Adipose tissue-derived extracellular vesicles in Diabetes-Associated Endothelial Dysfunction. We are currently studying the structure and content (lipids, proteins, and genetic material) of adipose tissue-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) and their impact on endothelial cell biology. Targets in this pathway include endothelial cell caveolae and the associated signaling including endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and insulin receptor (IR). We employ cutting-edge techniques such as transmission electron microscopy (TEM), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), confocal microscopy, and TIRF (Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence) microscopy to study mechanisms of EV uptake by endothelial cells and changes in caveolar dynamics and endothelial cell function in response to EVs isolated from patients with distinct metabolic profiles.
-
Project 3
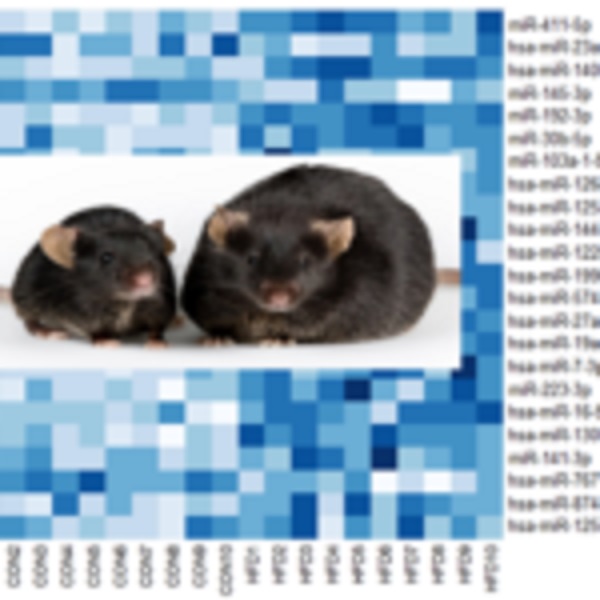
High-fat diet-induced epigenetic changes (DNA methylation, histone modifications, and miRNAs) and role of bioactive food components on reversing them. We are testing the effects of short chain amino acids, sulforaphane, and methyl donor micronutrients such folate, vitamin B12, and methionine. Specific targets include HDAC (histone deacetylase) activity in adipose tissues and skeletal muscles, tissue and vascular remodeling factors, endothelial glycocalyx, vasoactive mediators, and mechanosensitive Ca2+ channels on endothelial cell surface.
-
Project 4
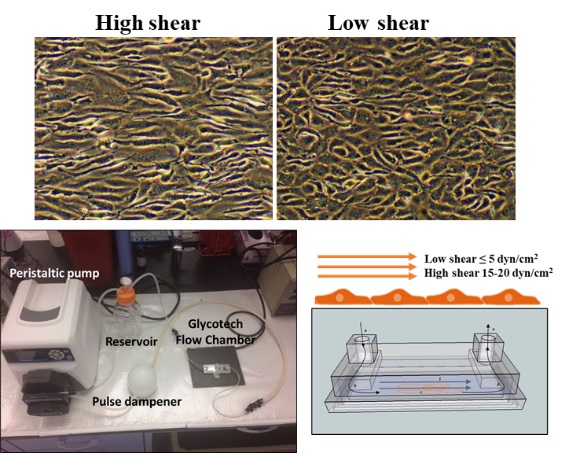
Effect of shear stress on mitigating HDAC-mediated downregulation of endothelial GLUT1 and glucose transport. Endothelial cells are regularly exposed to shear stress and convert these mechanical stimuli to chemical and intracellular signaling (mechano-transduction). The magnitude of shear stress increases during physical activity. The major goal in this project is to conduct experiments on endothelial cells cultured under low versus high shear stress and investigate HDAC activity, GLUT1 transcription and surface localization, and endothelial cell glucose uptake. The knowledge gained from this comparison will advance our understanding of endothelial cell biology and identify valid targets to improve endothelial glucose uptake.
-
Project 5
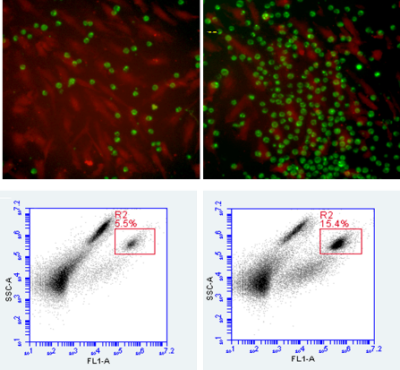
Role of adipose tissue-derived extracellular vesicles in promoting breast cancer metastasis. The risk of breast cancer metastasis is more significant in obese women, yet this connection is still not well understood. Fat depots represent key secretory organs, and much of this secretome can be found in adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). The purpose of this pilot is to investigate the role of EVs in communicating the unhealthy milieu of dysfunctional adipose tissues to endothelial cells, creating a premetastatic niche for circulating tumor cells.
Lab Publications Heading link
-
2021
Mahmoud AM, Gonçalves da Silva, Delgado L, Hwang CL, Severin R, Sanchez-Johnsen L, Borghi-Silva A, Elokda A, Arena R, Phillips SA. Effects of exercise mode on improving cardiovascular function and cardiorespiratory fitness after bariatric surgery: A narrative review. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
Ali MM, Hassan C, Masrur M, Bianco FM, Naquiallah D, Mirza I, Frederick P, Fernandes ET, Giulianotti CP, Gangemi A, Phillips SA, Mahmoud AM. Adipose Tissue Hypoxia Correlates with Adipokine Hypomethylation and Vascular Dysfunction. Biomedicines. 2021 Aug 18;9(8):1034.
Mahmoud AM, Ali MM. High Glucose and Advanced Glycation End Products Induce CD147-mediated MMP Activity in Human Adipocytes. Cells. 2021 Aug 16;10(8):2098.
Al-Alem U, Mahmoud AM, Batai K, Shah-Williams E, Gann PH, Kittles R, Rauscher GH. Genetic variation and immunohistochemical localization of the glucocorticoid receptor in breast cancer cases from the Breast Cancer Care in Chicago cohort. Cancers 2021, 13(10), 2261.
Ali MM, Qureshi M, Hassan C, Masrur M, Bianco FM, Frederick P, Cristoforo GP, Gangemi A, Phillips SA, and Mahmoud AM. DNA Methylation Profile of Genes Involved in Inflammation and Autoimmunity Correlates with Vascular Function in Morbidly Obese Adults. Epigenetics, 2021 Jan 25:1-17
Ali MA, Hassan C, Masrur M, Bianco FM, Mahmoud AM. Circulating and Adipose Tissue Levels of CD147 are Linked to Vascular Dysfunction in Obese Diabetic Adults. American Heart Association Annual Scientific Sessions, 2021
Ali, M., Mirza, I., Hassan, C., Masrur, M., Bianco, F., Fernandes, E., Cristoforo, G., Gangemi, A., Phillips, S. and Mahmoud, AM. Alcohol Consumption and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Morbidly Obese Individuals. The FASEB Journal, 35, 2021
Ali MM, Hassan C, Masrur M, Bianco FM, Mahmoud AM. Circulating and Adipose Tissue Levels of CD147 Are Linked to Vascular Dysfunction in Obese Diabetic Adults. Circulation 144 (Suppl-1), A10777
-
2020
Ali MM, Qureshi M, Hassan C, Masrur M, Bianco FM, Frederick P, Cristoforo GP, Gangemi A, Phillips SA, and Mahmoud AM. DNA Methylation Profile of Genes Involved in Inflammation and Autoimmunity Correlates with Vascular Function in Morbidly Obese Adults. Epigenetics, 2021 Jan 25:1-17
Haloul M, Vinjamuri SJ, Naquiallah D, Mirza MI, Qureshi M, Hassan C, Masrur M, Bianco FM, Frederick P, Cristoforo GP, Gangemi A, Ali MM, Phillips SA, and Mahmoud AM. Hyperhomocysteinemia and Low Folate and Vitamin B12 are Associated with Vascular Dysfunction and Impaired Nitric Oxide Sensitivity in Morbidly Obese Patients. Nutrients. 2020 Jul 7;12(7):2014
Hwang CL, Ranieri C, Szczurek MR, Ellythy AM, Elokda A, Mahmoud AM, Phillips SA. The Effect of Low-Carbohydrate Diet on Macrovascular and Microvascular Endothelial Function is Not Affected by the Provision of Caloric Restriction in Women with Obesity: A Randomized Study. Nutrients 2020, 12(6), 1649
Ali MA, Phillips SA, Mahmoud AM. HIF1α/TET1 Pathway Mediates Hypoxia-induced Adipocytokine Promoter Hypomethylation in Human Adipocytes. Cells. 2020 Jan 6;9(1).
CL Hwang, C Ranieri, AM Mahmoud, SA Phillips. Low-Carbohydrate Diet Does Not Improve Flow-Mediated Dilation In Obese Adults. Circulation 140 (Suppl_1), A17096-A17096
Ali MA, Naquiallah D, Hassan C, Masrur M, Bianco FM, Frederick P, Cristoforo GP, Gangemi A, Phillips SA, and Mahmoud AM. Aberrant DNA Methylation as a Contributor to Obesity-associated Vascular Dysfunction. American Diabetes Association, 80th Scientific Sessions June 12 – 16, 2020, Chicago, Illinois. Available as an E-poster
Ali MA, Naquiallah D, Hassan C, Masrur M, Bianco FM, Frederick P, Cristoforo GP, Gangemi A, Phillips SA, and Mahmoud AM. Obesity-associated Hypoxia Contributes to Aberrant Methylation of Genes Implicated in Inflammation and vascular Function. Experimental Biology 2020 San Diego, California, USA. April 4-7, 2020. The FASEB Journal 34 (S1), 1-1
JM Alim, K Hoskins, AM Mahmoud, V Macias, A Kadjascy-Balla, Rauscher GH. Racial disparity in the prevalence of BCL-2 expression and associations with breast cancer survival in the Breast Cancer Care in Chicago study. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention 29 (6)
Ali MA, Naquiallah D, Hassan C, Masrur M, Bianco FM, Frederick P, Cristoforo GP, Gangemi A, Phillips SA, and Mahmoud AM. Obesity-associated Hypoxia Contributes to Aberrant Methylation of Genes Implicated in Inflammation and vascular Function. Oral Abstract Sessions. Midwest Clinical and Translational Research Meeting of CSCTR and MWAFMR, Chicago April 2-3, 2020
-
2019
Ali MA, Phillips SA, Mahmoud AM. HIF1α/TET1 Pathway Mediates Hypoxia-induced Adipocytokine Promoter Hypomethylation in Human Adipocytes. Cells. 2020 Jan 6;9(1).
Mahmoud AM, Szczurek M, Hassan C, Masrur M, Gangemi A, Phillips SA. Vitamin D Improves Nitric Oxide-dependent Vasodilation in Adipose Tissue Arterioles from Bariatric Surgery Patients. Nutrients. 2019 Oct 18;11(10). pii: E2521. doi: 10.3390/nu11102521.
Mahmoud AM, Hwang CL, Szczurek M, Bian JT, Ranieri C, Gutterman D and Phillips SA, Low-fat Diet designed for Weight Loss but not Weight Maintenance Improves Nitric Oxide-dependent Arteriolar Vasodilation in Obese Adults. Nutrients, 2019 Jun 14;11(6)
Mahmoud AM, Ali MM. Methyl Donor Micronutrients that Modify DNA Methylation and Cancer Outcome. Nutrients. 2019 Mar 13;11(3).
Ali MM, Mahmoud AM, Phillips SA. Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Histone Deacetylase in Oxidative Stress-induced Degradation of the Endothelial Glycocalyx. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Mar 1;316(3):H647-H663
Severin R, Sabbahi A, Mahmoud AM, Arena R, Phillips SA. Precision Medicine in Weight Loss and Healthy Living. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases. 2019 Jan 2. pii: S0033-0620(18)30264-0
Mahmoud AM, Ali MA, Bianco FM, Gangemi A, Masrur M, Hassan C, Phillips SA. Obesity-associated Hypoxia Contributes to Aberrant Methylation of Genes Implicated in Inflammation and vascular Function. 2nd Global Conference on Cardiovascular Research and Clinical Cardiology, 2019 Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
Hwang CL, Ranieri C, Mahmoud AM, Phillips SA. Low-Carbohydrate Diet Does Not Improve Flow- Mediated Dilation In Obese Adults. Circulation 140 (Suppl_1), A17096-A17096
Mahmoud AM, Ali MA, Naquiallah D, Severin R, Bianco FM, Gangemi A, Masrur M, Hassan C, Phillips SA. Adipose Tissue-produced Inflammation Contributes to the Impaired Flow-Induced Dilations in Visceral and Subcutaneous Adipose Arterioles in Morbidly Obese Adults. American Heart Association Annual Meetings, 2018
Staff Bios Heading link
-
Staff Bios
Dina Naquiallah, MD, MPH, MHA
Research coordinatorImaduddin Mirza, BS
Research Assistant/coordinatorMohamed Hussein, MD
Postdoctoral Research AssistantHagar Ismail, MS
Research Assistant -
Student/Volunteers
Areij Mohamed
Undergraduate student
College of Liberal Arts and SciencesHania Deen
Undergraduate student
Honors CollegeCaroline Dobosz
Undergraduate Student
Honors CollegeAmier Munasser
Undergraduate Student
Honors CollegeHumza Ahmed
Undergraduate Student
College of Liberal Arts and SciencesUzma Abdulbaseer
Undergraduate Student
College of Liberal Arts and Sciences