Also known as Dr. Loeb's Lab
Lab Overview Heading link
Dr. Loeb is a practicing neurologist, epileptologist, and neuroscientist who currently holds the John S. Garvin Chair, Professor, and Head of the Department of Neurology and Rehabilitation. He received his A.B. in Chemistry, M.D., and Ph.D. from the University of Chicago. After completing a residency in Neurology at the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, he joined the faculty of Harvard Medical School where he also had fellowship training in epilepsy at Harvard’s Beth Israel Deaconess Hospital.
Dr. Loeb conducted postdoctoral work in the Department of Neurobiology at Harvard Medical School with Dr. Gerald Fischbach where he became interested in how understanding early neural development can teach us what goes wrong in human disease and suggest new treatments. This has led him to develop and patent a targeted drug that blocks neuregulin signaling and shows promise in degenerative disease that blocks neural inflammation, such as ALS. He also directs a project to develop new treatments for human epilepsy through a large-scale systems biology project to link the genes, molecular and cellular signals that underlie the abnormal electrical activities that characterize this common neurological disorder.
Dr. Loeb is currently the director of the University of Illinois NeuroRepository and the Faculty Director of the Biomedical Informatics Core of the Center for Clinical and Translational Science where he explores how big data can help find ways to understand and treat human brain disorders.
Research Heading link
Our Laboratory makes a concerted effort to develop a strong understanding of the developing nervous system AND human tissue samples as a means to understand human neurological disease and develop novel treatments. These are currently the areas of focus.
-
Translating trophic factors in development to treatment of disease
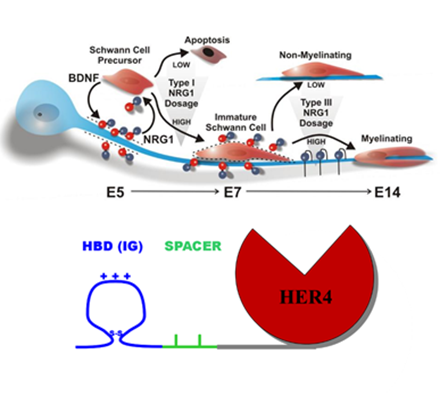
We have worked to understand the early molecular events regulating the formation of synapses and axo-glial junctions in the developing nervous system. Our analysis centers on how soluble regulatory factors such as the neuregulins and neurotrophins work together with neuronal activity to orchestrate developmen t. Many studies underway are examining how neuregulins themselves are regulated during development through regulation of their transcription, post-translational processing and association with the evolving extracellular matrix.
One of our missions is to take principles learned from early development and apply these toward understanding and treating human diseases including ALS, where have discovered an important link between environmental triggers and genetics. We have further developed a new way to target pharmaceuticals to specific regions in the body and have developed and are commercializing fusion protein drugs that use this technology that we plan to advance to clinical trials. In addition to ALS, diseases of interest include Multiple Sclerosis, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Cancer
-
Brain stones and water softeners
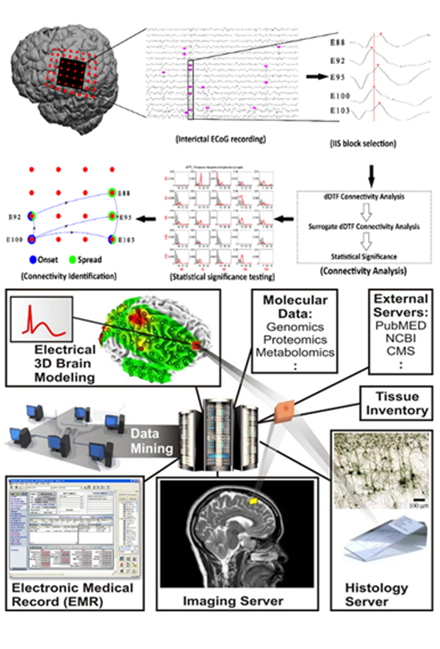
Another major focus of our group is to decode what makes focal regions of human brain epileptic. We have taken a SYSTEMS BIOLOGY and functional genomic approach using novel experimental and bioinformatic technologies to map genes, proteins, and small molecule expression patterns to the electrical abnormalities in human epileptic tissues removed during epilepsy surgery. We have found similarities between focal epileptic regions and normal mechanisms that enhance learning and memory paving the way for the identification of new therapeutic targets in human epilepsy.
Bioengineering collaborations have led to new approaches to map epileptic spikes and seizures, new imaging biomarkers, and new therapeutic ap proaches using animal models of epilepsy with long term video EEG recordings. Through this program, we have developed a collaborative project called the ‘Systems Biology of Epilepsy Project’ now housed in the University of Illinois NeuroRepository to bring together a wide range of physiological, molecular (genomic, proteomic, and metabolomic), and clinical aspects of human epilepsy into a centralized database. This project has led to the development of a larger, University-wide project to create novel, far-reaching data systems that link a wide variety of clinical and scientific data together focusing on the human brain.
-
Systems Biology of Human Epilepsy and Development of Novel Treatments
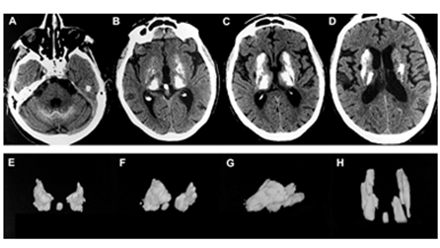
Dr. Loeb has pioneered the clinical use of bone drugs called bisphosphonates to treat brain disorders which have abnormal calcifications. These diseases share common clinical features depending on where the calcifications are and include Parkinsonian, Epileptic, Migraines, and Behavioral symptoms. This interest has led Dr. Loeb to examine clinical and treatment development for diseases ranging from Fahr’s, Sturge Weber, Tuberous Sclerosis, and Neurocysticercosis. Research progress include natural history of disease and drug development.
People Heading link
The team at the lab.
-
Research Scientists and Faculty
-
Graduate Students
News Heading link
Publications Heading link
- Pandey DK, Levy J, Serafini A, Habibi M, Song W, Shafer PO, Loeb JA.(2019) Self-management skills and behaviors, self-efficacy, and quality of life in people with epilepsy from underserved populations. Epilepsy Behav. 98:258-265
- Luat AF, Juhász C, Loeb JA, Chugani HT, Falchek SJ, Jain B, Greene-Roethke C, Amlie-Lefond C, Ball KL, Davis A, Pinto A.(2019)Neurological Complications of Sturge-Weber Syndrome: Current Status and Unmet Needs. Pediatr Neurol. 98:31-38.
- Maharathi, B, Loeb JA, Patton J (2019) Central sulcus is a barrier to causal propagation in epileptic networks. Conference: 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC)/ accepted in Press.
- Maharathi B, Wlodarski R, Bagla S, Asano E, Hua J, Patton J, Loeb JA. (2018) Interictal spike connectivity in human epileptic cortex. Neurophysiol. 130:270-79. [Selected for journal cover illustration/ Won the Mary Brazier Young Investigator Paper Award].
- Schram S, Chuang D, Schmidt G, Piponov H, Helder C, Kerns J, Gonzalez M, Song F, Loeb JA. (2018) Mutant SOD1 prevents normal functional recovery through enhanced glial activation and loss of motor neuron innervation after peripheral nerve injury, Dis. 124:469-478.
- De la Torre AJ, Luat AF, Juhász C, Ho ML, Argersinger, DP, Cavuoto KM, Enriquez-Algeciras M, Tikkanen S, North P, Burkhart CN, Chugani HT, Ball KL, Pinto AL, Loeb JA (2018) A Multidisciplinary Consensus for Clinical Care and Research Needs for Sturge-Weber Syndrome, Neurol., 84:11-20.
- Herrick JA, Maharathi B, Kim JS, Abundis GG, Garg A, Gonzales I, Saavedra H, Bustos JA, Garcia HH, Loeb JA (2018) Inflammation is a key risk factor for persistent seizures in neurocysticercosis, Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 5(5): 630–639.
- Keren-Aviram G, Dachet F, Bagla S, Balan K, Loeb JA, Dratz EA (2018) Proteomic analysis of human epileptic neocortex predicts vascular and glial changes in epileptic regions, Plos One, 13(4):e0195639.
- Liu J, Allender E, Wang J, Simpson EH, Loeb JA, Song F (2018) Slowing disease progression in the SOD1 mouse model of ALS by blocking neuregulin-induced microglial activation, Neurobiol Dis. 111:118-126.
- Wu HC, Dachet F, Ghoddoussi F, Bagla S, Fuerst D, Stanley JA, Galloway MP, Loeb JA (2017) Altered metabolomic-genomic signature: A non-invasive biomarker of epilepsy, Epilepsia 58(9):1626-1636.
- Jozwiak S, Becker A, Cepeda C, Engel J Jr, Gnatkovsky V, Huberfeld G, Kaya M, Kobow K, Simonato M, Loeb JA (2017) WONOEP appraisal: Development of epilepsy biomarkers-What we can learn from our patients? Epilepsia. 58(6):951-961.
- Wang J, Song F, Loeb JA (2017) Neuregulin1 fine-tunes pre-, post-, and perisynaptic neuromuscular junction development. Dev Dyn. 246(5):368-380.
- Barry G, Briggs JA, Hwang DW, Nayler SP, Fortuna PR, Jonkhout N, Dachet F, Maag JL, Mestdagh P, Singh EM, Avesson L, Kaczorowski DC, Ozturk E, Jones NC, Vetter I, Arriola-Martinez L, Hu J, Franco GR, Warn VM, Gong A, Dinger ME, Rigo F, Lipovich L, Morris MJ, O’Brien TJ, Lee DS, Loeb JA, Blackshaw S, Mattick JS, Wolvetang EJ, (2017) The long non-coding RNA NEAT1 is responsive to neuronal activity and is associated with hyperexcitability states. Sci Rep. 7:40127.
- Maharathi B, Loeb JA, Patton J (2016) Estimation of resting state effective connectivity in epilepsy using direct-directed transfer function, Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2016:716-719.
- Comi AM, Sahin M, Hammill A, Kaplan EH, Juhasz C, North P, Ball KL, Levin AV, Cohen B, Morris J, Lo W, Roach ES, (and 52 collaborators including Loeb JA) (2016) Leveraging a Sturge-Weber Gene Discovery: An Agenda for Future Research Pedatri Neurol 58:12-24.
- Serafini R, Dettloff S, Loeb JA (2016) Neocortical slices from adult chronic epileptic rats exhibit discharges of higher voltages and broader spread, Neuroscience 322:509-24, PMID: 26892299.
- Mittal S, Barkmeier DT, Hua J, Pai DS, Fuerst D, Basha M, Loeb JA, Shah AK (2015) Intracranial EEG analysis in tumor-related epilepsy: Evidence of distant epileptic abnormalities. Clin Neurophys 127:238-44. PMID:26493495.
- Boutros NN, Bowyer S, Wang J, Urfy MZ, Loeb JA (2015) Epilepsy spectrum disorders: A concept in need of validation or refutation, Med Hypothesis 85:656-63, PMID: 26319642.
- Nash TE, Mahanty S, Loeb JA, Theodore WH, Friedman A, Sander JW, Singh EG, Cavalheiro E, Del Brutto OH, Takayanagui O, Fleury A, Verastegui DM, Preux PM, Montano S, Pretell EJ, White, Jr., EH, Gonzales AE, Gilman R, Garcia HH, (2015) In response: Multifactorial basis of epilepsy in patients with neurocysticercosis, Epilepsia, 56:975-6.
- Wang J, Hmadcha A, Zakarian V, Song F, Loeb JA. (2015) Rapid transient isoform-specific neuregulin1 transcription in motor neurons is regulated by neurotrophic factors and axon-target interactions. Mol Cell Neurosci. 68:73-81.
- Serafini R, Andrade R, Loeb JA. (2015) Coalescence of deep and superficial epileptic foci into larger discharge units in adult rat neocortex. Neuroscience 292:148-158.
- Dachet F., Bagla S., Karen-Aviram G, Morton A, Balan K, Saadat L, Valyi-Nagy T, Kupsky W., Song F, Dratz E, Loeb JA (2015) Predicting novel histopathological microlesions in human epileptic brain through transcriptional clustering Brain, 138:356-70.




