
Angela L. Tyner, PhD
Professor
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics
Contact
Office Phone:
Lab
Building & Room:
312-996-8181
Email:
Related Sites:
Major Interests Heading link
I have had a long-standing interest in epithelial biology, signaling, and cancer. Our research focuses on the intracellular epithelial tyrosine kinase Protein Tyrosine Kinase 6 (PTK6, also referred to as the Breast Tumor Kinase BRK, or the SRC-related Intestinal Kinase Sik), which my laboratory was first to identify in the mouse (Siyanova et al., 1994). We established that PTK6 has context dependent functions that depend on the tissue/cell type of expression, intracellular localization, and its activation status. PTK6 has both enzymatic and adaptor functions. Although nuclear PTK6 is associated with differentiation and growth arrest, we have demonstrated that active membrane-associated PTK6 promotes the epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cell transformation. Disruption of Ptk6 impairs tumor development in mouse models of prostate, breast, and skin cancer, indicating that targeting PTK6 in some cancers may have therapeutic benefits. We showed that the small molecule drug vemurafenib (PLX4032) inhibits PTK6 activity and signaling, and reduced PTK6-mediated prostate tumor growth.
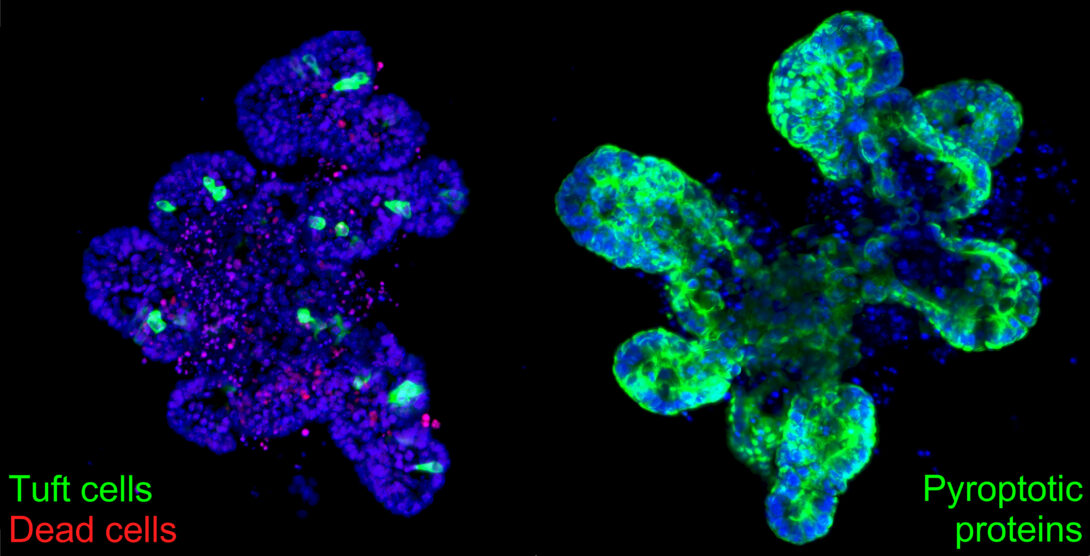
PTK6 regulates differentiation and cell turnover in the normal intestine. It has kinase-dependent and -independent functions and may act as a tumor suppressor or oncogene depending on conditions. New data demonstrate a role for PTK6 in regulating intestinal tuft cells and tuft cell expansion and indicate that PTK6 is a regulator of innate immunity and inflammation in the intestine. Ptk6-/- male but not female mice exhibit impaired tuft cell expansion and reduced IL-25 expression following exposure to succinate and provide a novel model for studying sex bias in innate immunity, which has relevance to fighting inflections, autoimmune disease and cancer.
Current studies are focused on determining how PTK6 contributes to tuft cell activation and sex-bias in innate immunity. We are also interested in further elucidating mechanisms by which PTK6 signaling promotes development and progression of prostate cancer.
Honors & Awards Heading link
UIC University Scholar (2017-2020)
Selected Publications
Gilic, M.B. and A.L. Tyner, Targeting ProteinTyrosine Kinase 6 in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2020. 1874(2): p. 188432.
Alwanian, W.M. and A.L. Tyner, Protein Tyrosine Kinase 6 signaling in prostate cancer. Am J Clin Exp Urol, 2020. 8(1): p. 1-8.
Wozniak, D.J., et al., Vemurafenib Inhibits Active PTK6 in PTEN-null Prostate Tumor Cells. Mol Cancer Ther, 2019. 18(5): p. 937-946..
Wozniak, D.J., et al., PTEN is a protein phosphatase that targets active PTK6 and inhibits PTK6 oncogenic signaling in prostate cancer. Nat Commun, 2017. 8(1): p. 1508.
Education
PhD, University of Chicago
Postdoctoral Training, Princeton University