Ehrlichia
Obligately intracellular Gram-negative bacteria Heading link
arget Cells: myeloid cells, hepatocytes, endothelial cells
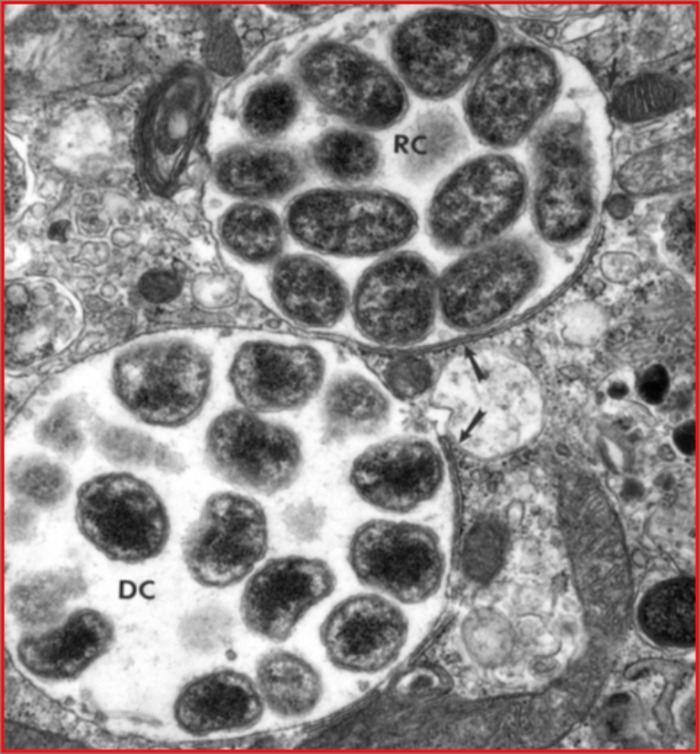
Ehrlichia reside in a phagosome within infected cells in two forms Reticulate and Dense core forms: EM picture
Ehrlichia lack LPS and peptidoglycan
Ehrlichia hijack host cell cholesterol to enter and replicate within target cells.
Ehrlichia exploit autophagy protein to obtain nutrients for their survival and replication.
Have type 1 and type IV secretion systems and & several secreted tandem repeat proteins
Ismail N, Bloch KC, McBride JW. Human ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis. Clin Lab Med. 2010 Mar;30(1):261-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2009.10.004.
Human Monocytic Ehrlichiosis Heading link
For more information about Ehrlichiosis, please visit the CDC website.
Life Cycle Heading link
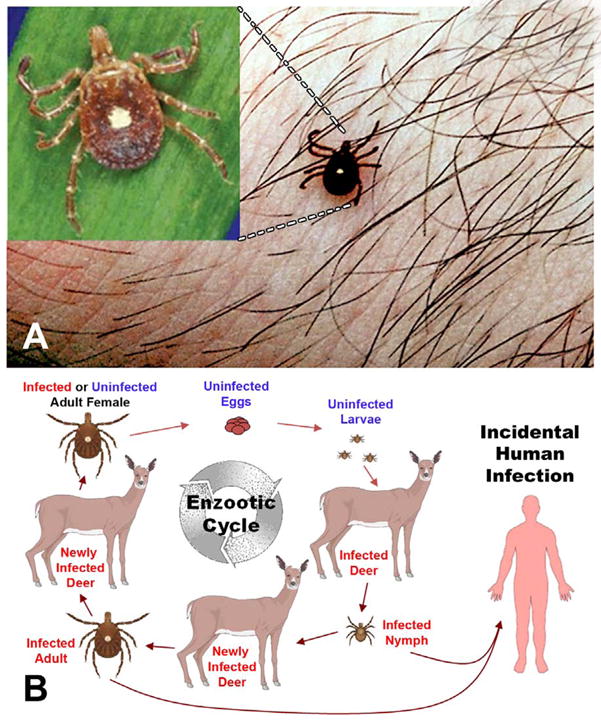
Life Cycle of Amblyomma americanum that transmit the agent of human monocytic ehrlichiosis
Ismail N, Bloch KC, McBride JW. Human ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis. Clin Lab Med. 2010 Mar;30(1):261-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2009.10.004.
Animal Model of Ehrlichiosis Heading link
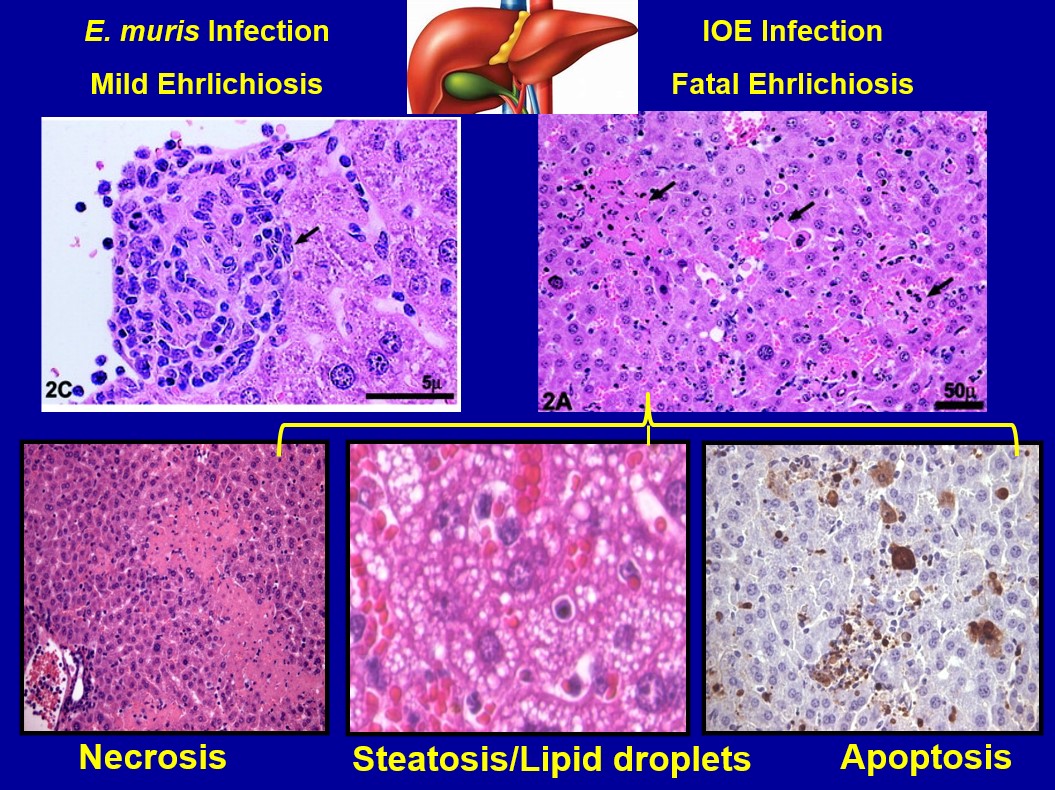
Ismail N, Bloch KC, McBride JW. Human ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis. Clin Lab Med. 2010 Mar;30(1):261-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2009.10.004.
Challenges in Ehrlichiosis Heading link
Challenges in Diagnosis
- Nonspecific clinical manifestation
- Lack of gold standard laboratory test limitations of serology, PCR, culture
Challenges in Treatment
- Resistance to commonly used antibiotics for Gram negative bacteria
- Late Doxycycline treatment is ineffective
Challenges in Prevention
- Vaccine is not available.
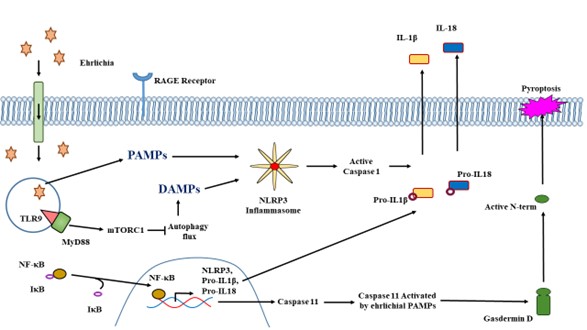
Model of inflammasome activation via canonical and non-canonical pathways Heading link
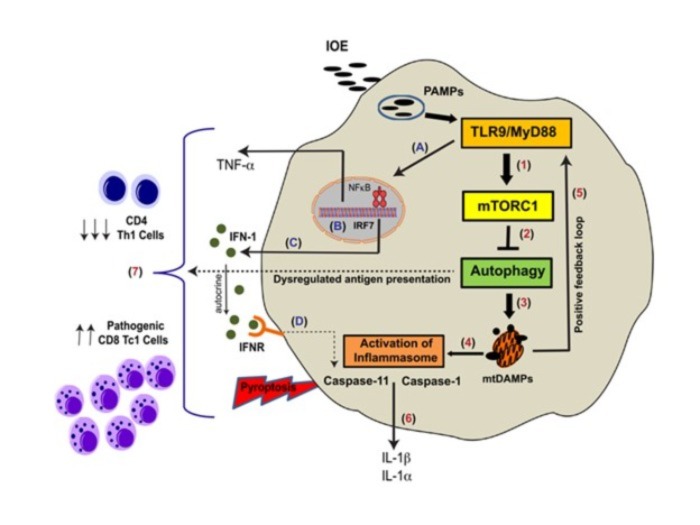
Ismail N, Sharma A, Soong L, Walker DH. Review: Protective Immunity and Immunopathology of Ehrlichiosis. Zoonoses (Burlingt). 2022 Jan 6;2(1):10.15212/zoonoses-2022-0009. doi: 10.15212/zoonoses-2022-0009