COVID-19
Since the first cases of COVID-19 were identified in the United States in early 2020, there have been nearly 100 million cases reported (Centers for Disease Control). COVID-19 continues to have a large presence in the United States and has devastated its citizens, especially those in underserved and vulnerable populations. This necessitates intervention through expanded access to testing, earlier diagnosis, and providing more accurate messaging about COVID-19.
Rapid Acceleration in Diagnostics in Underserved Populations (RADx-UP) Heading link
RADX-UP-NIH Initiatives:
The National institutes of Health created the RADx-UP initiative as a call for scientists across the nation to bring innovative ideas for new COVID-19 testing strategies to make tests more accurate, accessible, and easy to use. To learn more, visit the NIH website.
RADX NIH Projects
The National Institutes of Health developed programs under RADx to achieve their overarching goal of making COVID-19 testing more accurate, accessible, and easy to use. These programs include: RADx Tech, RADx Underserved Populations (RADx-UP), RADx Radical, and RADx Advanced Technology Platforms. To learn more about each individual program, visit the NIH website.
NIH Funded Projects Heading link
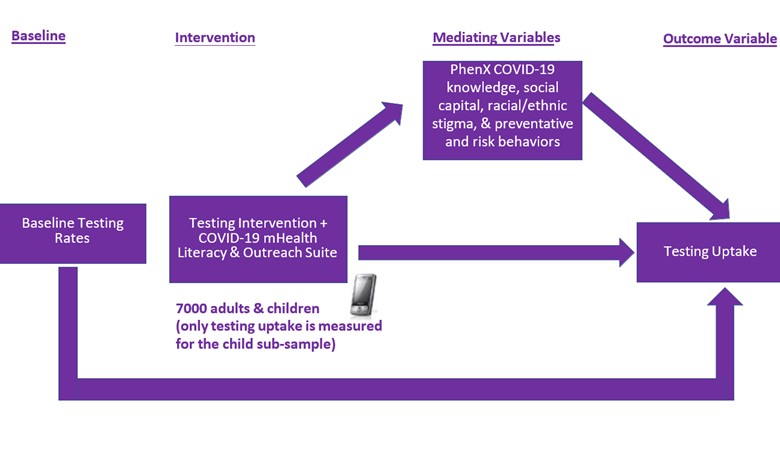
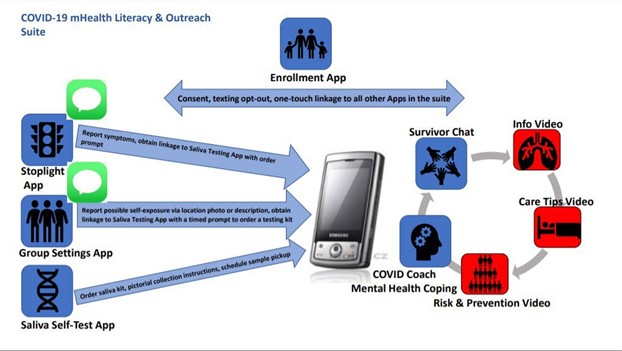
Investigating the effectiveness of COVID-19 testing choices, community engagement, and culturally embedded mHealth literacy delivery in a medically underserved, community-based sample
This study is examining whether offering people in Cook County and Suburban Cook County with COVID-19 information and access to a painless COVID-19 diagnostic test will result in higher rates of COVID-19 testing through Rapid Acceleration in Diagnostics in Underserved Populations (RADx-Up). RADx-UP, an initiative funded by the NIH, works to expand COVID-19 testing for underserved and/or vulnerable populations. This study not only seeks to increase testing and address testing barriers in the Chicago area, but it also aims to understand the dynamics, transmission, and evolution of the virus by analyzing COVID-19 positive samples.
Application of NOVEL RT-LAMP Assay for Direct Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva Heading link
Salivary/respiratory aerosols and droplets are recognized as a significant factor in person-to-person transmission of COVID-19. This study is being conducted with the purpose of testing symptomatic and asymptomatic people residing in in Cook County and Suburban Cook County through self-collected nasal swab samples and saliva samples. Data and specimens collected will aid in the evaluation of the clinical utilization of self-collected saliva-based test using an innovative LAMP technique that offers not only high accuracy in detection of virus levels in saliva, but also the potential for rapid, easy, and non-invasive self-collection.