Lab Director Heading link
Lab Overview Heading link
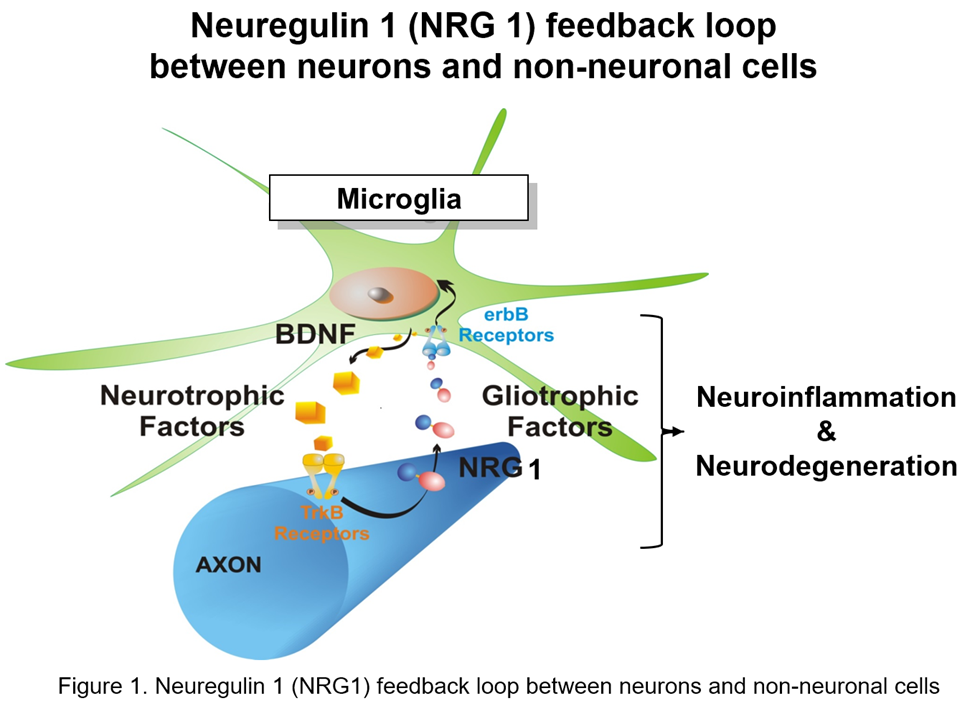
Song’s lab studies the pathology and therapeutics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), multiple sclerosis (MS), and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) by focusing on the communication and interaction between neuron and non-neuronal cells (Figure 1). The overall hypothesis is that soluble forms of neuregulin 1 (NRG1, gliotrophic factor) are naturally released from the ongoing neurodegeneration of neurons/axons to promote CNS innate immune cells (microglia) activation in the central nervous system (CNS).
Microglia Heading link
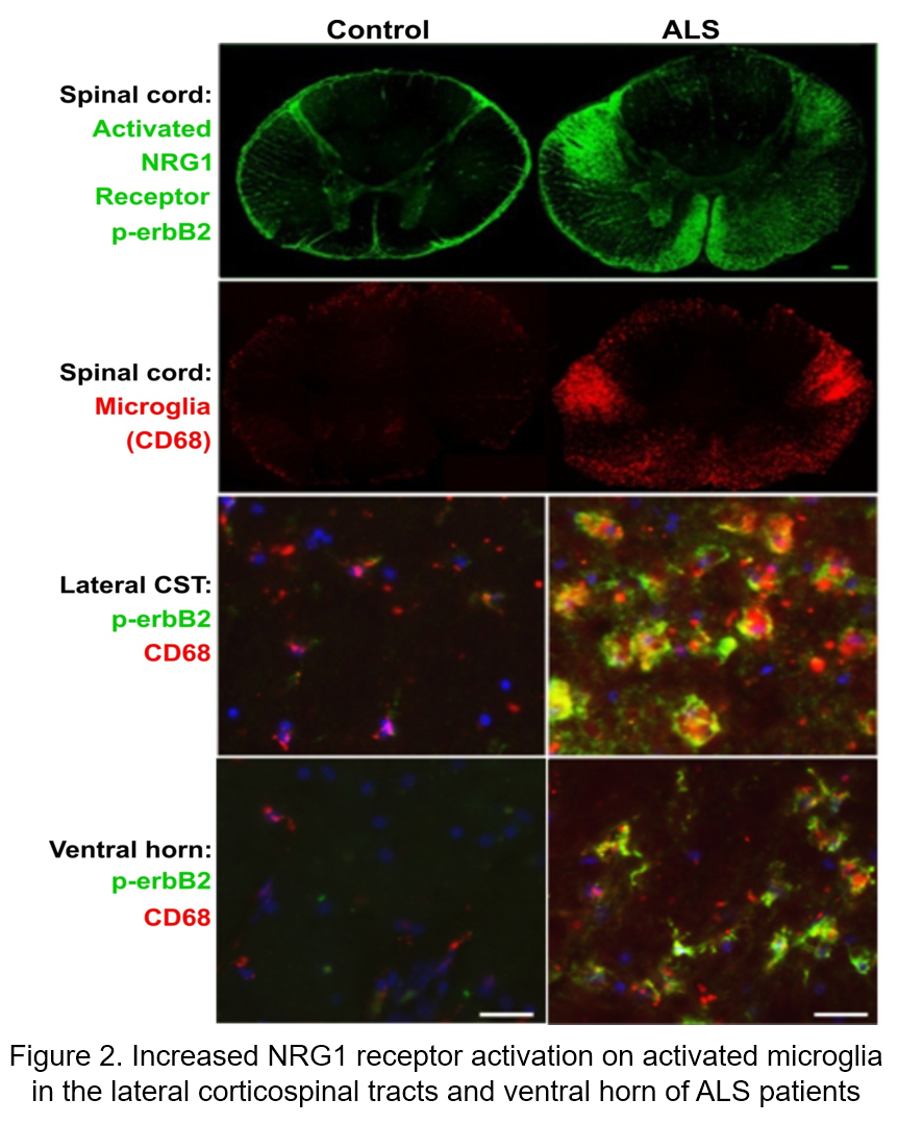
Microglia are brain-resident myeloid cells, which serve as the primary players in neuroinflammation, that influence the progression of neurodegenerative diseases from altering phagocytosis and synaptic pruning to producing inflammatory cytokines and changes in trophic support. Neuronal released abnormal NRG1 activates NRG1 receptors (Herbs/ErbBs) on surrounding microglia resulting in localized neuron/axon degeneration, and spreads the degeneration throughout the CNS, including the brain and spinal cord (ventral horn and the corticospinal tracts Figure 2).
Selected Publications Heading link
- Liu J, Geraghty JR, Schram S, Cropper HC, Lei J, Loeb JA, *Fei Song. 10.1523/ENEURO.0422-23.2023
- Schram S, Loeb JA, *Song F. Disease propagation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): an interplay between genetics and environment. J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jun 6;17(1):175. PMID: 32505190.
- Dachet F, Liu J, Ravits J, *Song F. Predicting disease specific spinal motor neurons and glia in sporadic ALS. Neurobiol Dis. 2019. PMID: 31276795.
- Liu J, Allender E, Wang J, Simpson EH, Loeb JA, *Song F. Slowing disease progression in the SOD1 mouse model of ALS by blocking neuregulin-induced microglial activation. Neurobiol Dis. 2018 Mar;111:118-126. PMID: 29278738.
- Allender E, Deol H, Schram S, Maheras KJ, Gow A, Simpson EH, *Song F. Neuregulin1 modulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). J Neuroimmunol. 2018 May 15;318:56-64. PMID: 29534847.
- Wang J, Hmadcha A, Zakarian V, *Song F, Loeb JA. Rapid transient isoform-specific neuregulin1 transcription in motor neurons is regulated by neurotrophic factors and axon-target interactions. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015 Sep;68:73-81. PMID: 25913151.
- *Song F, Chiang P, Ravits J, Loeb JA. Activation of microglial neuregulin1 signaling in the corticospinal tracts of ALS patients with upper motor neuron signs. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener. 2014 Mar;15(1-2):77-83. PMID: 24229388.
- *Song F, Bandara M, Deol H, Loeb JA, Benjamins J, Lisak RP. Complexity of trophic factor signaling in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: differential expression of neurotrophic and gliotrophic factors. J Neuroimmunol. 2013 Sep 15;262(1-2):11-8. PMID: 23763772.
- *Song F, Chiang P, Wang J, Ravits J, Loeb JA. Aberrant neuregulin 1 signaling in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2012 Feb;71(2):104-15. PMID: 22249457.
- *Song F, Wardrop RM, Gienapp IE, Stuckman SS, Meyer AL, Shawler T, Whitacre CC. The Peyer’s patch is a critical immunoregulatory site for mucosal tolerance in experimental autoimmune encephalomylelitis (EAE). J Autoimmun. 2008 Jun;30(4):230-7. PMID: 18006271.
- *Song F, Guan Z, Gienapp IE, Shawler T, Benson J, Whitacre CC. The thymus plays a role in oral tolerance in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2006 Aug 1;177(3):1500-9. PMID: 16849456.
*Corresponding Author
